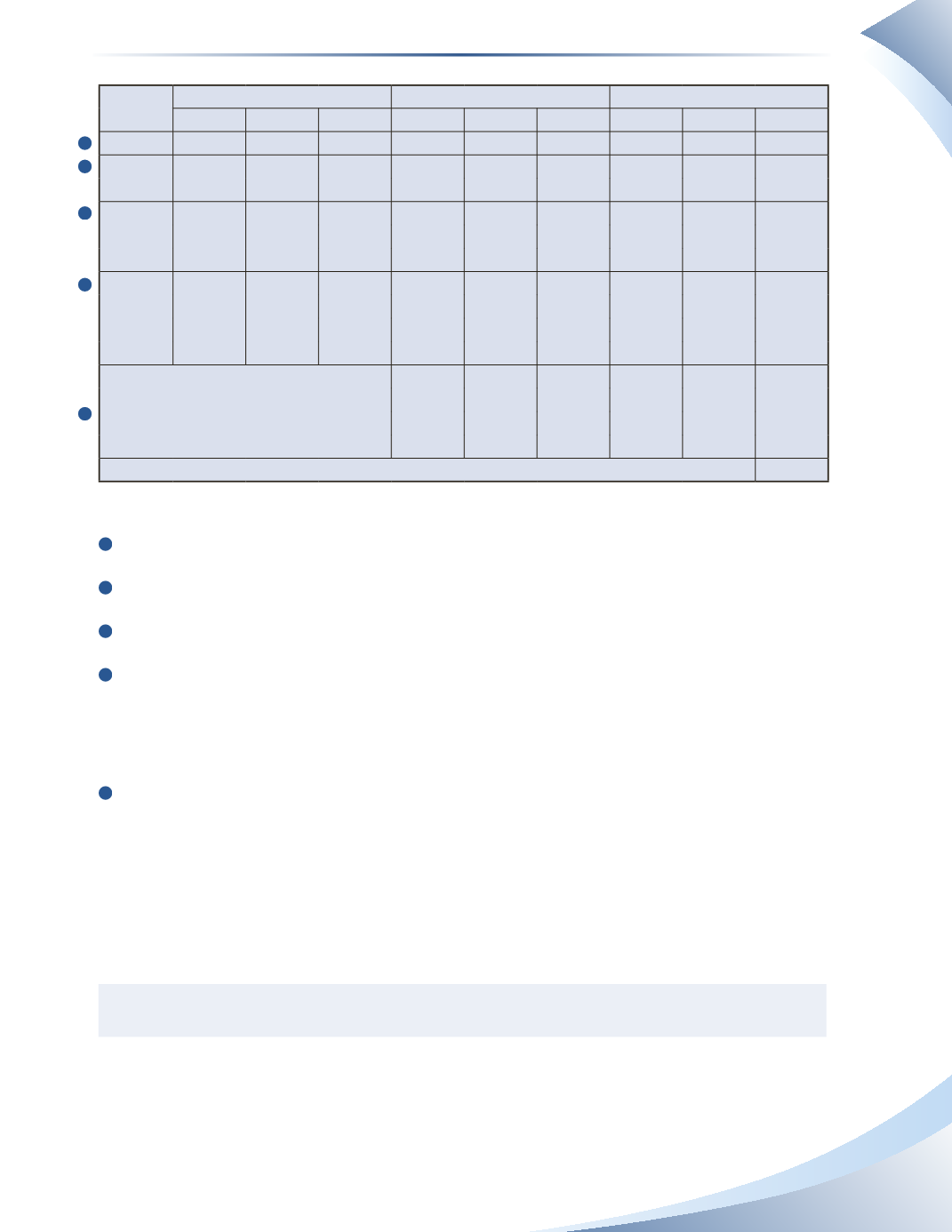
251
Date
Purchases
Sales
Balance
Quantity Unit Cost Value Quantity Unit Cost Value Quantity Unit Cost Value
March 1
10
$10
$100
March 5
50
$12
$600
10
$10
$100
50
$12
$600
March 15 40
$14
$560
10
$10
$100
50
$12
$600
40
$14
$560
March 19 20
$16
$320
10
$10
$100
50
$12
$600
40
$14
$560
20
$16
$320
Sales for the Month
10
$10
$100
50
$12
$600
5
$14
$70
35
$14 $490
20
$16 $320
Ending Inventory
$810
________________
FIGURE 8A.3
1
The purchase of 50 pens on March 5 is added to the value of inventory.
2
The purchase of 40 pens on March 15 is added to the value of inventory.
3
The purchase of 20 pens on March 19 is added to the value of inventory.
4
There was a total of 65 items sold (15 units + 40 units). Costs are taken from the balance
of inventory, starting with the first item at the top of the list. The entire amount of opening
inventory, the entire amount of the March 5 purchase, and five items from the March 15
purchase are considered sold. Total cost of goods sold is $770 ($100 + $600 + $70).
5
The value of ending inventory is made up of 35 pens remaining from the March 15 purchase
and the 20 pens remaining from the March 19 purchase.Total value of inventory is $810 ($490
+ $320).
UsingWeighted-Average Cost
When using the weighted-average cost method, the average cost per unit is only calculated once, at
the end of the period.This is done by using a table as shown in Figure 8A.4. Recall that
Average Unit Cost = Total Quantity ÷ Total Value
The opening balance and the transactions from Figure 8A.1 are listed in the table. At the bottom
of the figure is the value of ending inventory.
1
2
3
4
5
Chapter 8 Appendix
Inventory Valuation


