Chapter 3
The Accounting Framework
64
Private enterprises may choose to adhere to IFRS, or may follow the
Accounting Standards for
Private Enterprises (ASPE)
, developed by the AcSB. These standards are less complex and are
used only by private companies in Canada.
Both ASPE and IFRS conform to an underlying
conceptual framework
. This framework forms
the basis to determine how business transactions should be measured and reported. It ensures the
external users (e.g. shareholders) have the most consistent, reliable and useful information when
reviewing a company’s financial reports. Although it is not possible to create a specific rule for
every situation, the principles under the conceptual framework allow accountants to make appro-
priate decisions under different circumstances.This is referred to as
principles-based accounting
.
In other words, ASPE and IFRS are designed as guidelines and accountants are allowed to flexibly
apply these standards when preparing financial information. On the other hand, under
rules-based
accounting
, the accounting standards are stated as a list of specific, detailed rules that must be
followed when preparing financial information. To apply these rules, accountants have little room
to make their own judgments. Not every country adopts principles-based accounting. For example,
U.S. GAAP is primarily rules-based.
Next, we will examine the important characteristics, assumptions, and principles that form the
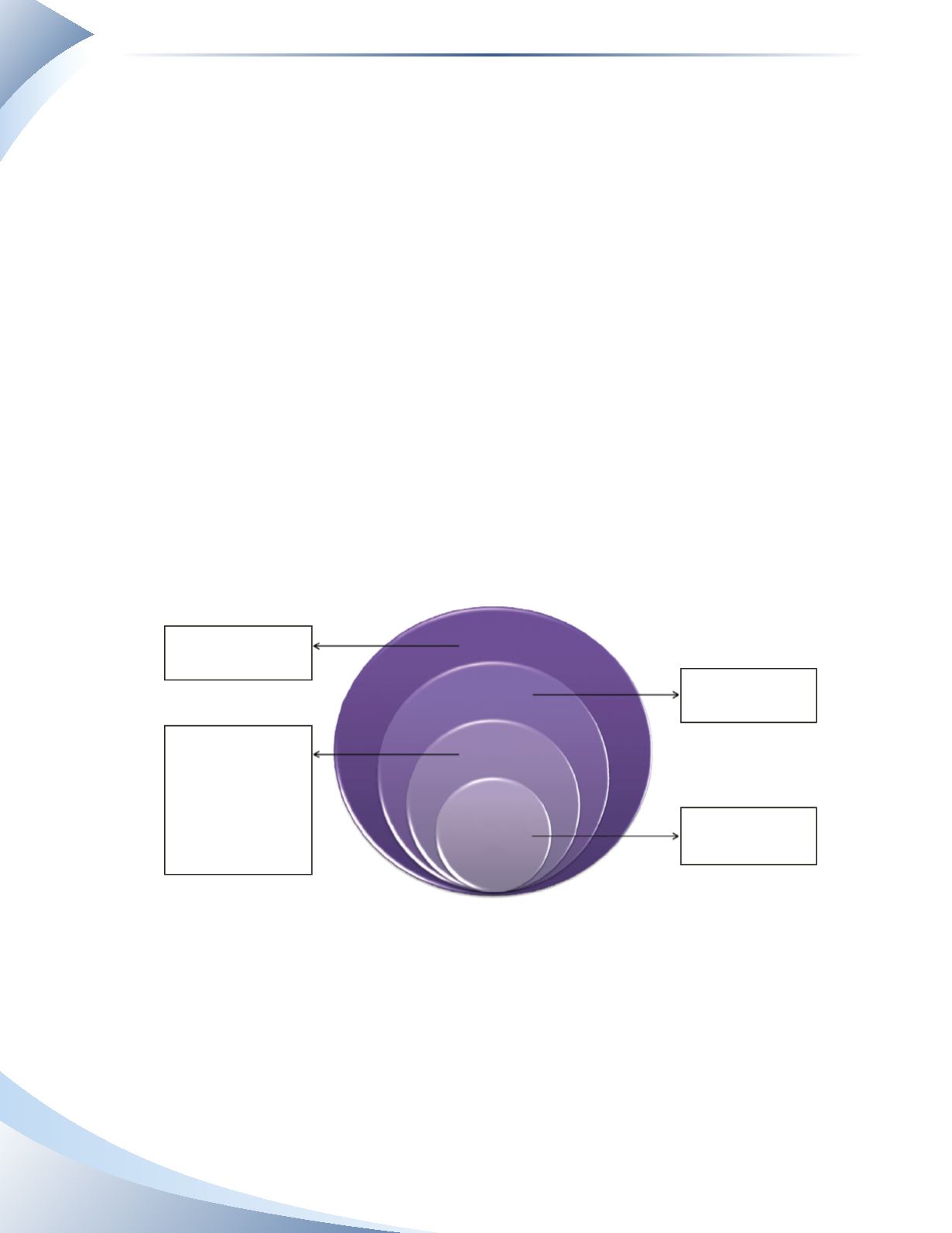
conceptual framework of accounting. Figure 3.5 illustrates the framework.
The Conceptual Framework of Accounting
To provide useful financial
information to a wide
range of users
Relevance, reliability,
understandability and
comparability
Assumptions
Principles
Business Entity, Going
Concern, Monetary Unit
Revenue Recognition,
Expense Recognition,
Consistency, Materiality,
Time Period, Disclosure
Assets, liabilities,
owner’s equity,
revenues and expenses
Objective of
Financial
Statements
Characteristics
of Financial
Information
Basic Assumptions
and Principles
Components of
Financial
Statements
______________
FIGURE 3.5
The fundamental objective of financial reporting is to provide useful and complete information to
the users. However, an underlying constraint in the accounting framework is the
cost constraint
.
It ensures that the value of reported financial information outweighs the costs incurred to report it,
even if the information would improve the accuracy and completeness of the financial statements.
For example, a company may find some information that is not required by accounting standards to
be somewhat useful, however it is costly to prepare. If the value of this information does not outweigh
the costs, the company should not prepare it.


