Chapter 1
Financial Statements: Personal Accounting
6
Accounting Periods
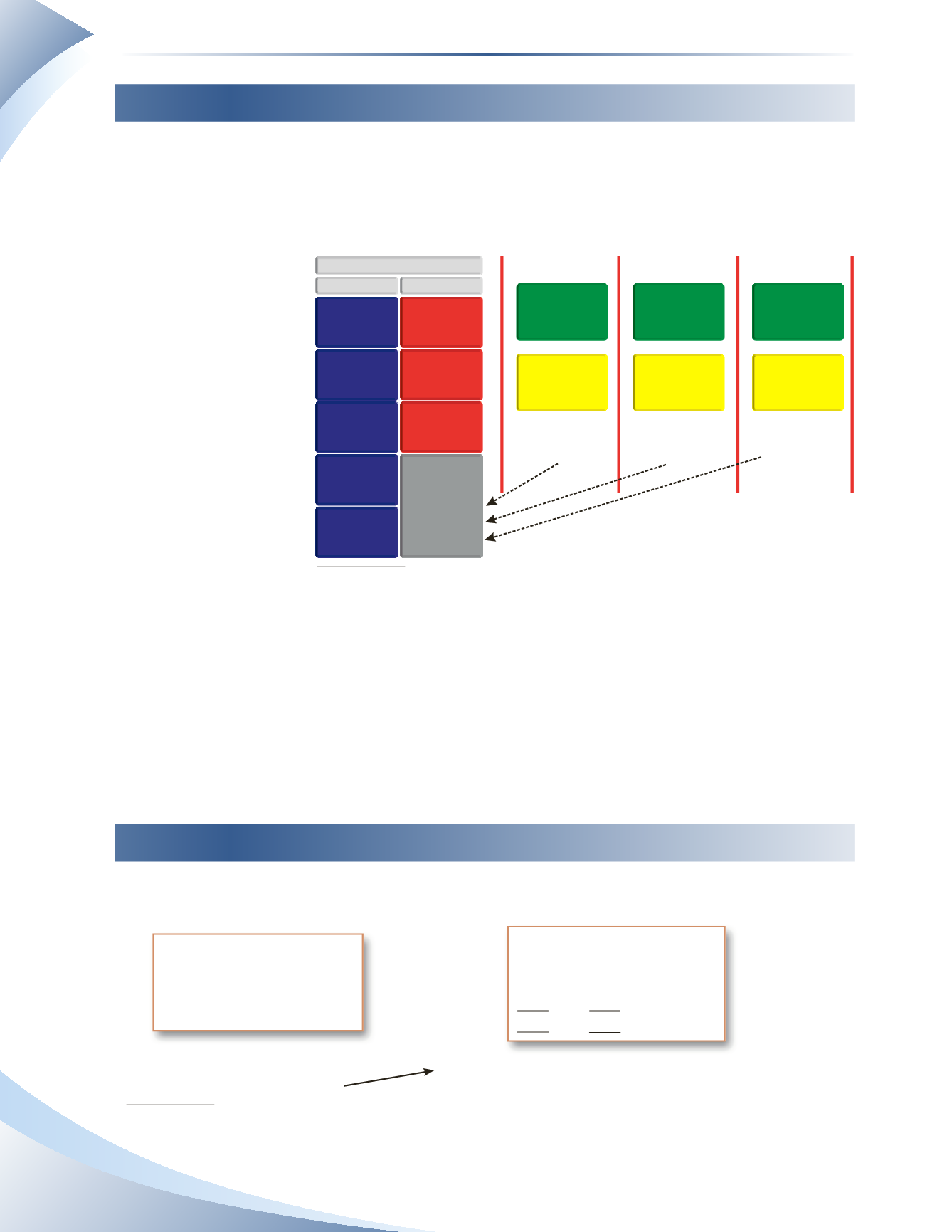
You can keep changing net worth continuously; however, for accounting purposes, it is more conve-
nient to record changes to net worth in separate periods. You can use any period you choose as an
accounting period. An
accounting period
is the time frame in which the financial statements are
prepared and can be
one year, six months
or one month, as
shown in Figure 1.8.
If you use a month
as your accounting
period, you can look
back at previous
months (periods) and
estimate what your
expenses and income
will be in the coming
months. You can also
estimate the surplus
or deficit you will
generate each month. If you are saving for a major purchase such as a car, a new computer or an
expensive entertainment system, you will be able to determine when you will have enough money
to buy the desired item or at least provide a down payment.
Some advantages of using monthly accounting periods for your personal financial statements include
•
tracking regular monthly living expenses (e.g. rent, cell phone)
•
frequently assessing realistic expectations
•
controlling errors effectively
The Accounting Equation
The accounting equation is shown in Figure 1.9.
FIGURE 1.9
Assets
Liabilities
$100
– $70
= 30
Net Worth
Assets
Liabilities
$100
$70
+ 30
Net Worth
$100
$100
If assets minus liabilities = net worth,
assets must equal liabilities plus net worth
then mathematically…
ASSETS
PERSONAL BALANCE SHEET
LIABILITIES
CASH
PREPAID
EXPENSES
CONTENTS OF
HOME
AUTOMOBILE
HOUSE
UNPAID
ACCOUNTS
MORTGAGE
LOANS
NETWORTH
January
February
PERSONAL INCOME STATEMENT
March
Surplus
(Deficit)
Surplus
(Deficit)
Surplus
(Deficit)
REVENUE
REVENUE
REVENUE
EXPENSES
EXPENSES
EXPENSES
–
–
–
=
=
=
increase or decrease in net worth
FIGURE 1.8


