206
Inventory: Merchandising Transactions
Chapter 7
Appendix
Purchases
When inventory is purchased for resale using a periodic inventory system the inventory account
is not debited. Instead, we debit an account called purchases on the income statement, which is
part of cost of goods sold. If the inventory was paid for on credit, then accounts payable is credited.
If the inventory was paid for with cash, then the
cash account is credited. In this example, Tools 4U
purchased inventory of $10,000 on January 1, 2016.
Assume all purchases and sales are made on account.
The purchases account is a temporary account located on the income statement as part of COGS. It
records all the inventory purchased by a company during a specific period of time under the periodic
inventory system.
The values of inventory and cost of goods sold are not adjusted until the end of the period when
the physical inventory count is taken. As a result, we need to track the costs related to inventory in
separate accounts.
Purchase Returns
Continuing with the example of Tools 4U, assume the company returned $300 worth of inventory to
its supplier. Instead of just crediting the purchases account, businesses that use a periodic inventory
system track these returns by using a temporary
contra account to purchases called
purchase returns
and allowances
.This new account is also part of cost
of goods sold. The journal entry to record the above
return is shown in Figure 7A.4.
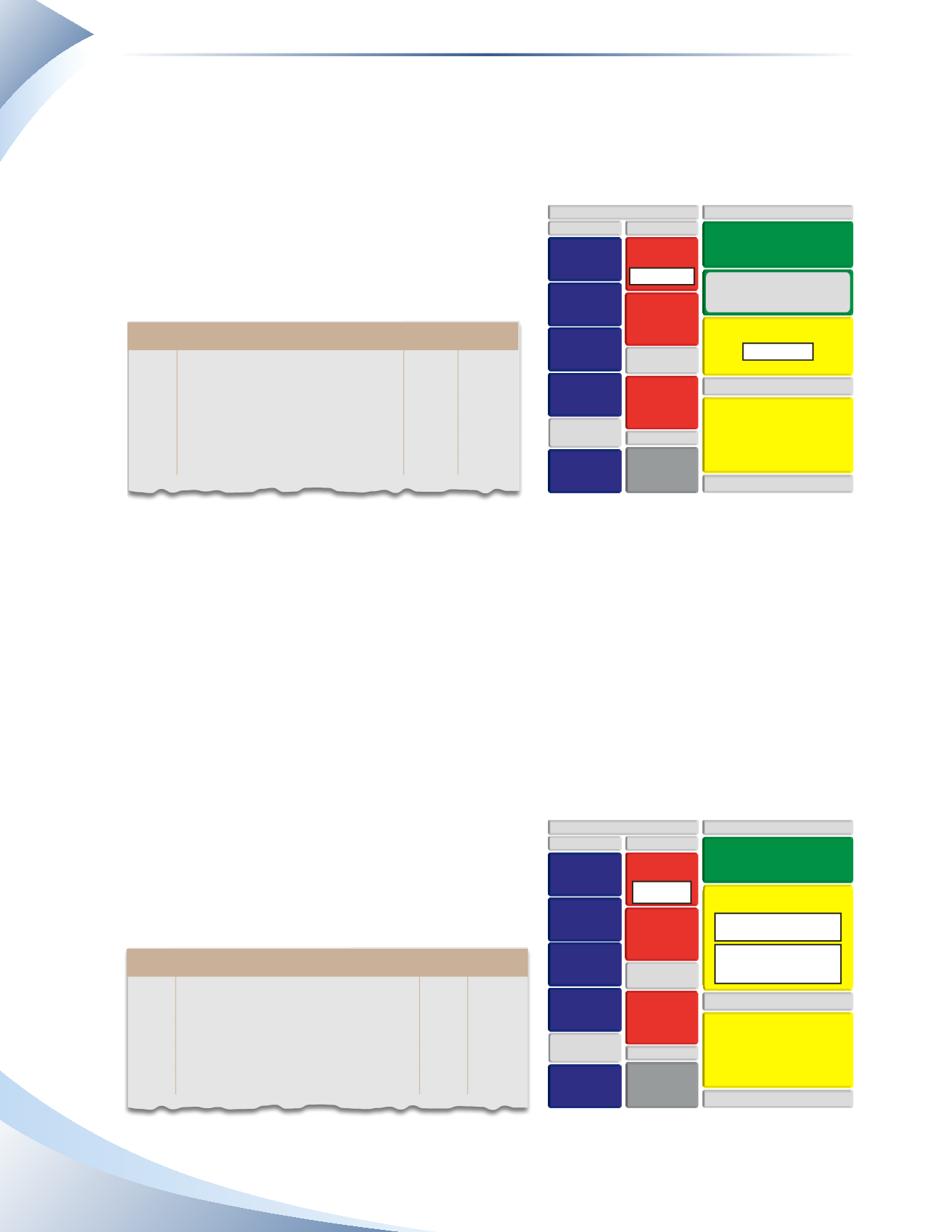
Journal
Page 1
date
2016
account title and explanation debit Credit
Jan 1 Purchases
10,000
Accounts Payable
10,000
Record purchase of inventory
____________
fIGuRe 7A.3
SALES RETURNS & ALLOWANCES
INCOME STATEMENT
GROSS PROFIT
OPERATING EXPENSES
SALES REVENUE
COST OF GOODS SOLD
BALANCE SHEET
CURRENT ASSETS
CASH
INVENTORY
ACCOUNTS
RECEIVABLE
PREPAID
EXPENSES
PROPERTY, PLANT
& EQUIPMENT
LONG-TERM
ASSETS
ACCOUNTS
PAYABLE
BANK LOAN
CURRENTLIABILITIES
UNEARNED
REVENUE
LONG-TERM
LIABILITIES
OWNER’S EQUITY
OWNER’S
CAPITAL
+ $10,000 CR
+ $10,000 DR
OPERATING INCOME
INCOME STATEMENT
GROSS PROFIT
OPERATING EXPENSES
SALES REVENUE
COST OF GOODS SOLD
BALANCE SHEET
CURRENT ASSETS
CASH
INVENTORY
ACCOUNTS
RECEIVABLE
PREPAID
EXPENSES
PROPERTY, PLANT
& EQUIPMENT
LONG-TERM
ASSETS
ACCOUNTS
PAYABLE
BANK LOAN
CURRENTLIABILITIES
UNEARNED
REVENUE
LONG-TERM
LIABILITIES
OWNER’S EQUITY
OWNER’S
CAPITAL
OPERATING INCOME
$10,000 CR
– $300 DR
PURCHASES
$10,000 DR
PURCHASE RETURNS
& ALLOWANCES
+ $300 CR
Journal
Page 1
date
2016
account title and explanation debit Credit
Jan 2 Accounts Payable
300
Purchase Returns and Allowances
300
Record purchase returns
____________
fIGuRe 7A.4


