Chapter 6
The Accounting Cycle: Statements and Closing Entries
141
4,900
250
250
+
-
-
-
+
+
10,200
1,500
1,500
+
PARISH, CAPITAL
DECREASE (DR)
INCREASE (CR)
-
5,300
+
TELEPHONE EXPENSE
DECREASE (DR)
INCREASE (CR)
-
ASSETS
LIABILITIES
SERVICE REVENUE
INCREASE (DR)
DECREASE (DR)
DECREASE (DR)
DECREASE (CR)
INCREASE (CR)
INCREASE (CR)
________________
Figure 6.10
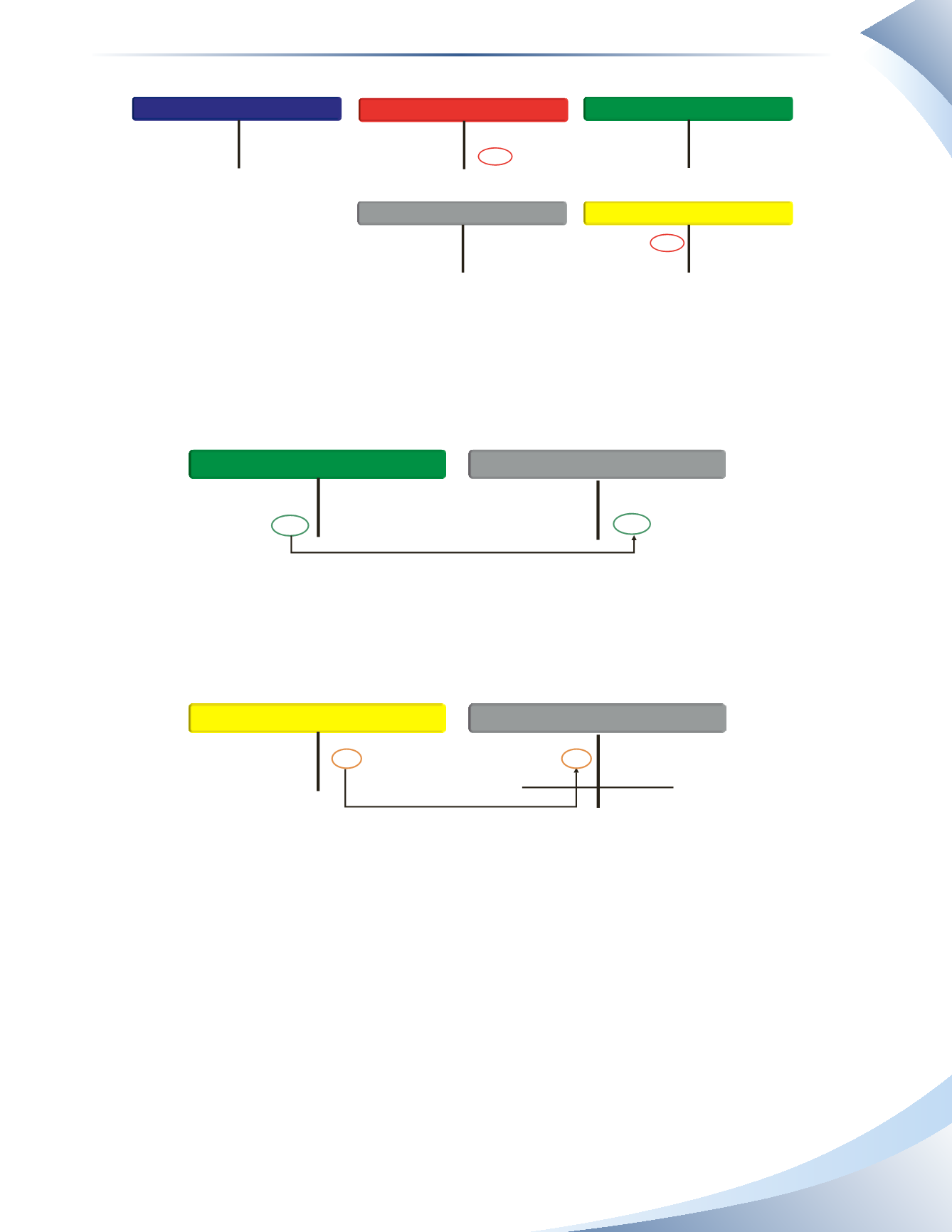
To get the balance sheet back into balance, owner’s capital must be updated with the revenue and
expense transactions. To do this, the revenue account must be closed by decreasing revenue and
increasing owner’s capital, as illustrated in Figure 6.11. The revenue account is now reduced to a
zero balance.
-
+
1,500 Current balance
1,500
+
PARISH, CAPITAL
DECREASE (DR)
INCREASE (CR)
-
5,300 Current balance
1,500
SERVICE REVENUE
DECREASE (DR)
INCREASE (CR)
________________
Figure 6.11
The expense account must also be closed by decreasing the expense and decreasing owner’s capital,
as illustrated in Figure 6.12.The expense account is now reduced to zero.
-
+
250
250
Current balance 250
+
PARISH, CAPITAL
DECREASE (DR)
INCREASE (CR)
-
5,300 Current balance
6,550 Ending balance
1,500
TELEPHONE EXPENSE
DECREASE (DR)
INCREASE (CR)
________________
Figure 6.12
The end result is that owner’s capital will have a new balance and assets will equal liabilities plus
equity.
To see how to close the books for MP Consulting, we will use the adjusted trial balance on the
worksheet, which shows all the balances we need. The adjusted trial balance is shown again in
Figure 6.13.


