Chapter 7
Inventory: Merchandising Transactions
181
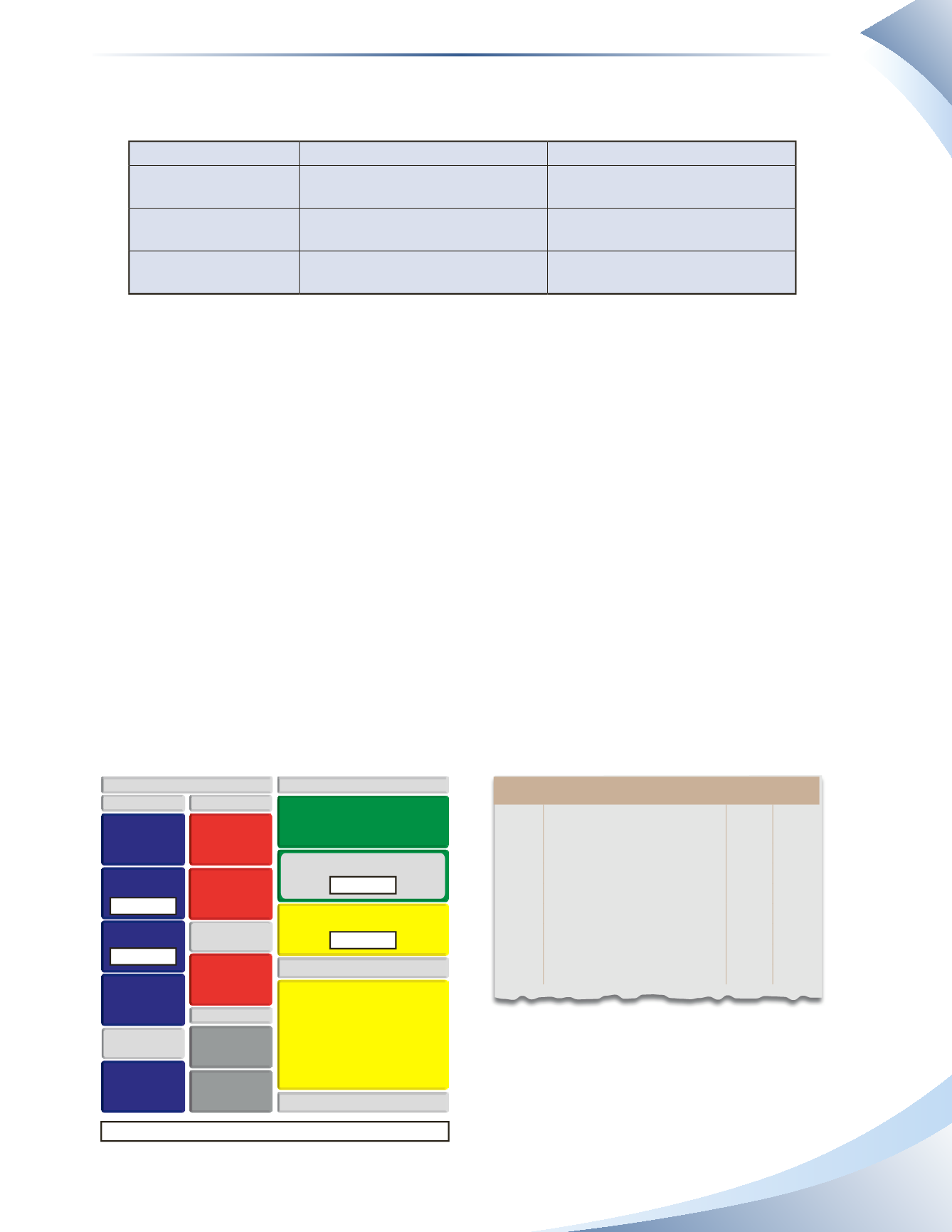
A summary of FOB shipping point and FOB destination is presented in Figure 7.14. Basically,
whoever pays for shipping owns the goods while they are being transported and bears the risk of loss.
FoB shipping Point
FoB destination
ownership Change
When goods leave the seller on a
common carrier
When goods arrive at the buyer’s
place of business
transportation Costs
Paid by the buyer and recorded in
inventory
Paid by the seller and recorded as
an expense
risk of loss
Buyer bears risk of loss during
transport
Seller bears risk of loss during
transport
______________
fIGuRe 7.14
Sales Returns
A merchandiser may have to deal with numerous returns from customers, and these returns
must be tracked over a period of time. High return levels may indicate serious problems with
the products being sold. Therefore, instead of reversing the revenue account with a debit when
recording returns, a contra-revenue account called
sales returns and allowances
is used to track
the amount of returns. Recall that contra means opposite and a contra account holds an opposite
normal balance of its related account.
Sales returns and allowances is a contra-revenue account with a normal debit balance. It is generally
used to record both sales returns and sales allowances.
Sales returns
occur when undesirable
products are returned to the seller.
Sales allowances
occur when the customer decides to keep such
undesirable products at a reduced price.
Continuing with our example, suppose that a customer returned $4,000 worth of undesirable goods
to Tools 4U (the original cost of the inventory was $3,000).There is nothing wrong with the goods
and they can be resold.The journal entries to record this return, using the contra-revenue account,
are shown in Figure 7.15. Note that two entries are required: one to record the reduction in sales
and accounts receivable (or cash, if applicable) and one to reverse the reduction of inventory.
Owner’s equity decreases by $1,000 (– $4,000 + $3,000)
SALES RETURNS & ALLOWANCES
INCOME STATEMENT
GROSS PROFIT
OPERATING EXPENSES
SALES REVENUE
COST OF GOODS SOLD
BALANCE SHEET
OPERATING INCOME (LOSS)
CURRENT ASSETS
CASH
INVENTORY
PREPAID
EXPENSES
PROPERTY, PLANT
& EQUIPMENT
ACCOUNTS
RECEIVABLE
LONG-TERM
ASSETS
ACCOUNTS
PAYABLE
BANK LOAN
OWNER’S EQUITY
CURRENT LIABILITIES
UNEARNED
REVENUE
LONG-TERM
LIABILITIES
– $4,000 CR
+ $4,000 DR
– $3,000 CR
+ $3,000 DR
OWNER’S
CAPITAL
OWNER’S
DRAWINGS
Journal
Page 1
date
2016
account title and explanation debit Credit
Jan 18 Sales Returns & Allowances
4,000
Accounts Receivable
4,000
Customer returned items
Jan 18 Inventory
3,000
Cost of Goods Sold
3,000
Restock returned inventory
______________
fIGuRe 7.15


