Chapter 10
Cash Controls
299
ACCOUNTS
RECEIVABLE
INCOME STATEMENT
SALES REVENUE
ACCOUNTS
PAYABLE
INVENTORY
ASSETS
BALANCE SHEET
LIABILITIES
CASH
OWNER’S EQUITY
UNEARNED
REVENUE
LOANS
PAYABLE
–
–
$400 CR
$10 CR
+
$400 DR
NSF
CHARGES
INSURANCE
RENT
SALARIES
+
$10 DR
COST OF GOODS SOLD
GROSS PROFIT
Journal
Page 1
Date
account title and
explanation
Debit Credit
2016
Jun 30 Accounts Receivable
400
Cash
400
NSF cheque returned by bank
Jun 30 NSF Charges Expense
10
Cash
10
Bank charge for NSF cheque
______________
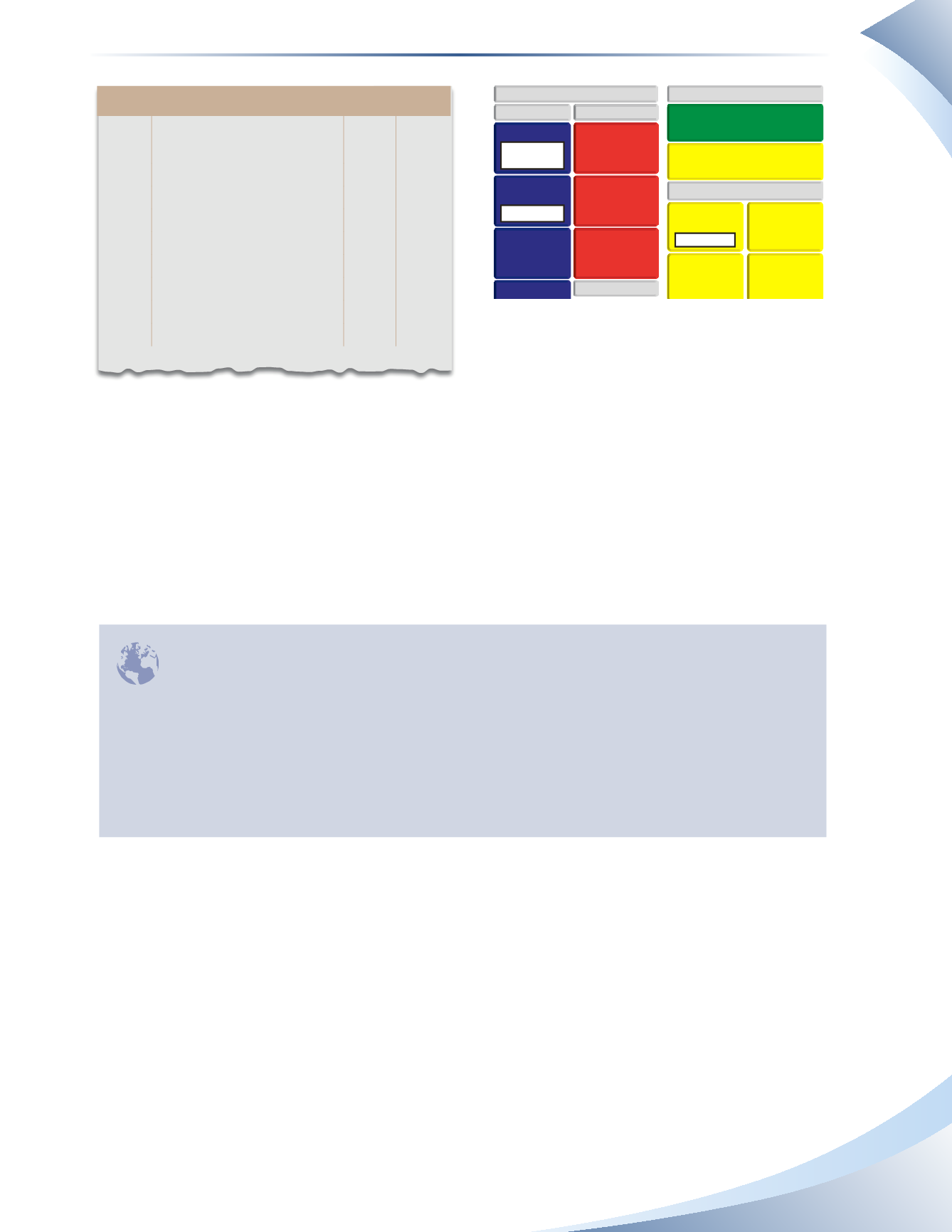
FIGURE 10.13
Notice that HR Clothing received a charge because the customer was unable to honour the cheque.
The company will not want to have to pay the extra fee for the customer’s error. HR Clothing will
create a new invoice to the customer, charging the customer an extra amount to cover the NSF
fee. Some companies just charge the customer the NSF fee it was charged, in this case $10. Other
companies charge the customer a flat fee greater than the NSF charge of $10 to cover the NSF fee
and to cover the administrative process of handling the NSF cheque.
Non-sufficient funds (NSF) cheques are commonly known as bad cheques or bounced cheques. In
our example, it is assumed that non-sufficient funds (NSF) cheques occur because the issuer of the
cheque does not have enough money in their own bank account to support the cheque. However,
NSF cheques can result from a variety of reasons including.
1. The issuer purposely cancels the cheque.
2. The account is frozen.
3. The account does not exist (i.e. the issuing party engaged in a fraudulent act).
4. The account is under investigation.
INTHE REAL WORLD
outstanding Deposits
An outstanding deposit is one that has been recorded in the company’s general ledger but not
shown on the bank statement.These are also referred to as
deposits in transit
.This can occur when
the company makes a deposit in the bank (perhaps using the night deposit box) on the last day of
the month, but the bank does not record the deposit until the following business day—in the next
month.The bank statement and the company’s ledger account may appear as shown in Figure 10.14.


